Parts of a Leaf With Their Structure and Functions
A leaf is a plant organ that is flat, thin and usually green in color. It is mostly found above the ground and remains attached to the stem.
The presence of pigment ‘chlorophyll’ makes the leaf green in color that helps to prepare food in plants through photosynthesis. Collectively, green leaves are called foliage.
What are the Different Parts of a Leaf
A typical leaf shows three main parts: 1) petiole, 2) leaf base, and 3) leaf blade or lamina, each performing specific functions.
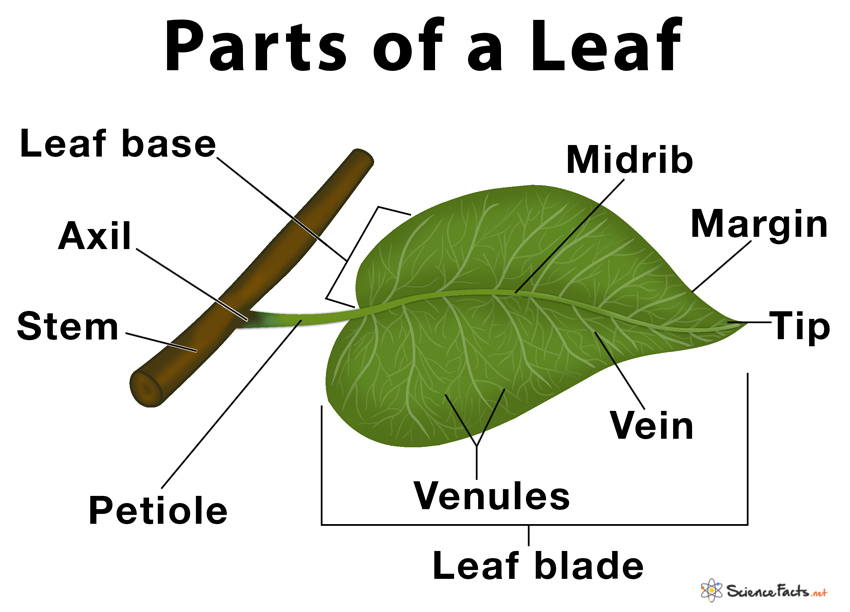
1. Petiole
It is the stalk that connects a leaf to the stem of the plant, it is made of complex conducting tissues called vascular tissues.
Functions
- Providing support to the leaf and keeps it erect
- Transporting water and nutrients absorbed by the roots to the leaves
- Transporting photosynthetic products from the leaves to the rest of the plant
2. Leaf Base
It is the lowermost part of a leaf, which is closest to the petiole.
Functions
- Helping in the attachment of the leaf to the stem
- It protects the young axillary bud
3. Leaf-blade or Lamina
It is the thin, flat part of the leaf that is typically green in color. It is further divided into three parts: i) leaf apex – the tip of the leaf blade, ii) leaf margin – the edge of the leaf and, iii) leaf veins – the small channels or capillaries, which are further subdivided into venules.
Functions
- Helping plants to prepare their food using raw materials like water, carbon dioxide, and minerals through photosynthesis
- Performing evaporation from the aerial parts of a plant by a process known as transpiration
- Veins and venues help in transporting water and nutrients throughout the leaf
FAQs
Q.1. What are the external parts of a plant leaf?
Ans. Petiole, leaf base, lamina, leaf apex, and leaf margin are the external parts of a leaf.
Q.2. What are the internal parts of a leaf?
Ans. Stomata, guard cells, epidermal cells, mesophyll cells, and vascular bundles (xylem, phloem, veins) are the internal parts of a leaf.
Q.3. What part of a leaf helps in gas exchange?
Ans. The gas exchange which involves the absorption of carbon dioxide and release of oxygen occurs through tiny pores present in the leaves called stomata.
Q4. What is a sessile leaf?
Ans. Leaves that are attached directly to the stem without the petioles are called sessile leaves. Saffron and Achyranthus plants have sessile leaves.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023




It’s very good. My name is Anantika Samal. I am studying in class 6. I am 12 years old.
i like this website but it needs to be simpler because i’m ten years old and this is too complicated.No offence.
I have a strange looking plant with flowers that look like wheat and have perpendicular leaves growing from the axil at the beginning of the petiole of the leaves. I crushed a leave and tasted and noticed that it was powerful as if it contained strong chemicals probably antioxidants. I searched on the web but was not successful, The plant is approximately five feet in height.
If you could provide me with an email address so that I can send you photos for identification would be great.
Thanks
Gd
Excellent
Good ☺️
How does plants make oyxgen and carbon dioxide
Plants take in oxygen that we breathe out and release carbon dioxide by way of photosynthesis
Firstly I would like to thank you for affording me the opportunity to applied and than thank you for sharing idea with me on the basis of the leafy.