Golgi Apparatus
Golgi apparatus, also named as Golgi complex, or Golgi body, is a series of flattened, stacked, membrane-bound cell organelle found in all animal and plant cells.
It receives molecules, changes them, and then categorizes and addresses them for transport to different cell parts. Golgi is thus analogous to the post office.
Due to its relatively large size, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles discovered. In 1897, Italian scientist Camillo Golgi first identified the Golgi apparatus. Later, in 1898 it was named after him.
Where is the Golgi Apparatus Located
The location of the Golgi varies depending on the cell type. In mammals, it is generally located within the cytoplasm adjacent to the nucleus and rough endoplasmic reticulum. In plants, it remains dispersed throughout the cytoplasm.
Structure of Golgi Apparatus
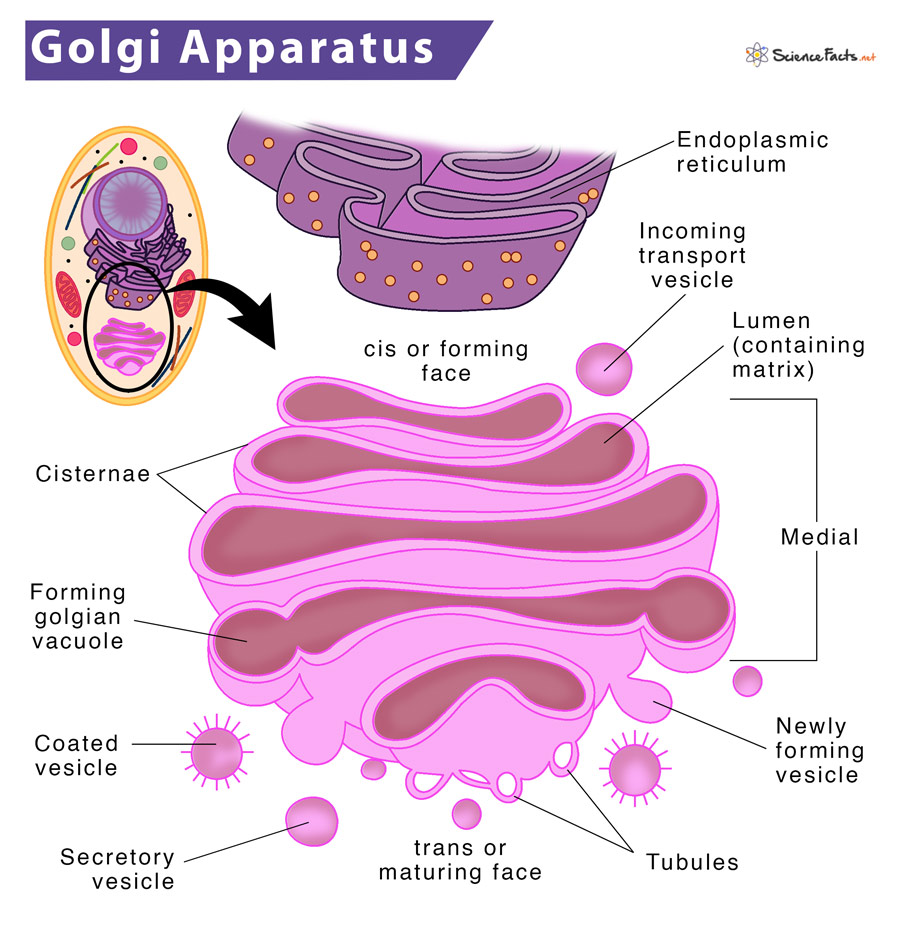
The Golgi apparatus is structurally very similar in both plant and animal cells. Under an electron microscope, Golgi is found to be composed of four functionally distinct parts:
What is the Golgi Apparatus Made of
They are made of the following parts:
1. Cisterna
They are flattened, cup-shaped, membrane-enclosed sacs held in parallel bundles or stacks that look like a stack of deflated balloons. Each sac contains a fluid called a matrix. Each cisterna is enclosed by a smooth unit membrane having a lumen with a thickness of 7.5 nm. There is a space of 20 to 30 nm between each cisterna. This gap is called inter-cisternal space, having a thin layer of cytoplasm containing parallel fibrils.
They are divided into three compartments: cis, medial and trans. The convex side facing the ER is called the cis-face or forming face; the center part is medial, and the concave side facing the plasma membrane is the trans-face or maturing face.
2. Tubules
They form a lace-like network towards the periphery, forming the internal connections between various cisternae, establishing connections between them, thus, synchronizing their functions. Tubules are 30 to 50 nm in diameter. They provide structural support to the organelle.
3. Vesicles
These tiny sacs of size 20-80 nm diameters bud off from tubules. They are of two types: coated and smooth vesicles.
4. Golgian Vacuoles
These are round vesicles or sacs, developing from the maturing face of cisternae, which get modified to vacuoles. These vacuoles bud off from the swollen edge of a cistern, finally budding off to form vesicles. Those vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes are known as lysosomes.
Functions of Golgi Apparatus
It is also referred to as the ‘traffic police’ of the cell, as it plays a crucial role in transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to their respective targeted destinations.
The critical roles of the Golgi apparatus found in both plant and animal cells are described below:
Processing and Sorting of Protein, Lipids, and Polysaccharides
Proteins from the ER first enter the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment and then the Golgi apparatus through the cis Golgi network. They then proceed to the medial and trans compartments of the Golgi stack, where most metabolic activities take place. The modified proteins and lipids move to the trans-Golgi network, which acts as a sorting and distribution center, directing the sorted molecules to their destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane, and finally, out of the cell.
Causing Post-translational Modifications
Post-translational modification and enzymatic processing, such as phosphorylation and glycosylation, happen near the membrane surface in Golgi bodies. In glycosylation, carbohydrate is added to proteins and lipids, forming glycoproteins and glycolipids. On the other hand, in phosphorylation, a phosphate group gets attached to an amino acid.
Forming Secretory Vesicles and Secretion
The products from the RER are transferred to Golgi for further processing. Subsequently, they are released from the cell through exocytosis.
The Golgi apparatus helps maintain cellular homeostasis by secreting proteins. These proteins are signaling peptides that help induce changes in gene expression in target cells, which regulate levels of metabolites and promote homeostasis.
Apart from the above functions, the Golgi apparatus is also involved in enzyme formation, such as the production of follicular fluid from granulosa cells of the ovary, synthesizing hormones, forming acrosomes, and producing lysosome and intracellular crystals.
Forming Cell Walls in Plants
In plants, it helps in forming the plant cell wall. During mitotic cell division, Golgi bodies form a cell plate at the center of the spindle. The cell plate gradually enlarges and gets thickened by the deposition of pectin, hemicellulose, and cellulose secreted by the Golgi complex.
FAQs
Ans. Golgi bodies prepare proteins for secretion.
Ans. Both lysosomes and Golgi bodies are cell organelles.
Ans. No, prokaryotes do not have Golgi apparatus.
Ans. No, bacteria do not have Golgi apparatus.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023