Denitrification
All life on earth relies on nitrogen, recycled through the global nitrogen cycle. Denitrification is the final step in the nitrogen cycle. The nitrogen fixed through nitrogen fixation is returned to the atmosphere as nitrogen gas. Thus, it helps to balance the amount of nitrogen in the ecosystems.
What is Denitrification
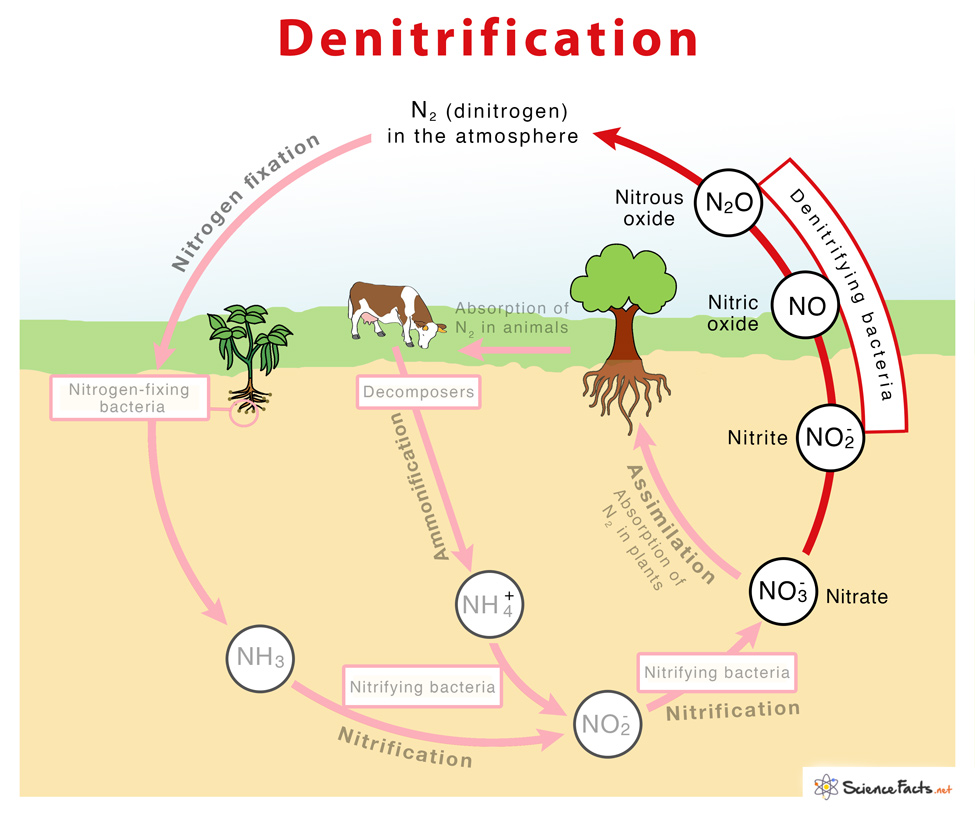
Denitrification is the biological process of sequential reduction of nitrogen oxides in the form of nitrate (NO3–) and nitrite (NO2–) to nitrogen-containing gases like nitric oxide (NO), nitrous oxide (N2O), and finally forming dinitrogen (N2). It is a microbial-mediated process.
NO3− → NO2− → NO → N2O → N2
The different steps of denitrification are carried out by enzymes nitrate reductase, nitrite reductase, nitric oxide reductase, and nitrous oxide reductase as shown below:
Denitrification proceeds through a combination of the following half-reactions:
- NO3− + 2 H+ + 2 e−→ NO₂− + H2O (by Nitrate reductase)
- NO₂− + 2 H+ + e− → NO + H2O (by Nitrite reductase)
- 2 NO + 2 H+ + 2 e− → N₂O + H2O (by Nitric oxide reductase)
- N₂O + 2 H+ + 2 e− → N₂ + H2O (by Nitrous oxide reductase)
The complete balanced equation of the entire process is given below:
2 NO3− + 10 e− + 12 H+ → N2 + 6 H2O
When Does it Occur
Facultative anaerobic bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, Escherichia, Enterobacter, Micrococcus, Rhizobium, and Bacillus, perform denitrification when depleting oxygen is forced to use nitrate as a substitute terminal electron acceptor instead of oxygen during respiration. Although primarily performed by heterotrophs, some autotrophs such as Thiobacillus denitrificans also perform denitrification.
Where does It Occur
Due to the high oxygen concentration in our atmosphere, denitrification only occurs in anaerobic environments where oxygen consumption exceeds the oxygen supply with high quantities of nitrate. These environments are found in warm and wet soils and groundwater, oil reservoirs, ocean corners, and sea floors.
Importance of Denitrification
Denitrification can be ecologically beneficial or detrimental, depending on when and where it occurs. It is the only point in the N cycle where fixed nitrogen reenters the atmosphere as N2. N2 fixers would use up the entire atmospheric nitrogen without denitrification, making the atmosphere devoid of nitrogen.
It is helpful in wastewater treatments. It helps remove unwanted nitrates from the wastewater effluents, reducing the chances that the water discharged from the treatment plants will cause undesirable consequences such as algal blooms (eutrophication). Denitrification is also essential in agriculture, where the loss of nitrates in fertilizer is detrimental and costly.
In contrast, the byproducts of denitrification, such as NO and N2O, contribute to the formation of smog and greenhouse gas-based climate change.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Saturday, February 26, 2022