Nitrogen Cycle
What is the nitrogen cycle?
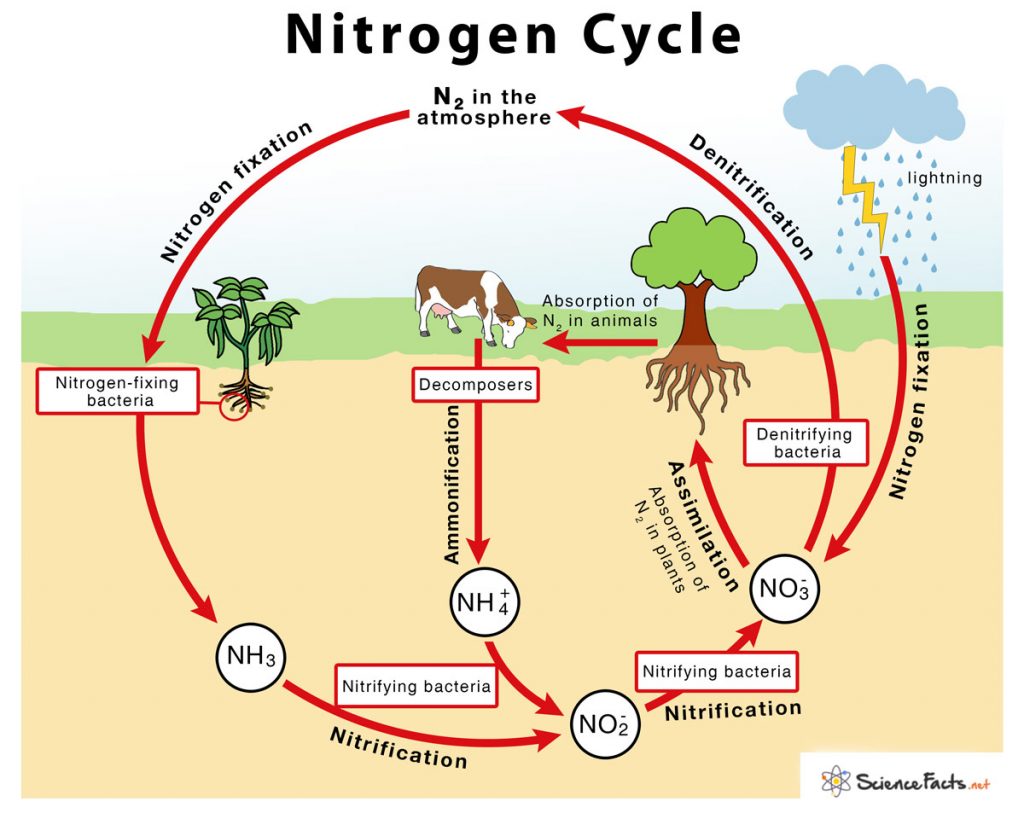
The series of processes by which nitrogen and its different forms are circulated and interconverted in nature with the help of living organisms is called the nitrogen cycle. It shows the path that nitrogen follows through the biogeochemical cycle using its storage reservoirs, such as the atmosphere, living organisms, and soil.
What are the main steps of the nitrogen cycle?
The entire process of the Nitrogen Cycle, one of the important biogeochemical cycle takes place in five stages:
1) Nitrogen Fixation by Bacteria – Converting inert atmospheric nitrogen (N2)into biologically available forms such as ammonia (NH3), nitrates, or nitrites
2) Nitrification by Bacteria – Converting ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate
3) Assimilation by Plants – Absorbing nitrogen from the soil and incorporating them in the plant and animal bodies
4) Ammonification by Decomposers – Converting the dead organic nitrogen of plants or animals back into ammonia
5) Denitrification by Denitrifiers – Reducingnitrates or nitrites and releasing gaseous nitrogen
What role do bacteria play in the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrogen fixation – Performed by two different groups of bacteria – a) symbiotic nitrogen fixers like Rhizobium, which keep a close association with the host leguminous plant, and b) free-living, non-symbiotic bacteria like Azotobacter.
Both these group of bacteria use specific enzymes to complete the biological nitrogen fixation process by the following reaction –
N2 + 8 H+ + 8 e− → 2 NH3 + H2
Nitrification – Performed by nitrifying bacteria in two steps –
i) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria such as Nitrosomonas species perform oxidation of ammonia to nitrite by the following reaction –
2NH4+ + 3O2 + 8 e− → 2 NO2– + 4H2 + 2H2O
ii) Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria such as Nitrobacter species perform oxidation of nitrite (NO2–) to nitrate (NO3–) by the following reaction –
2 NO3– + O2 → 2 NO3–
How are plants involved in the nitrogen cycle?
Plants help in the assimilation of nitrogen when they absorb it from the soil in the form of ammonia, nitrite ions, nitrate ions or ammonium ions to form plant and animal proteins. In leguminous plants such as pea and bean, the symbiotic association with Rhizobium helps to assimilate nitrogen directly in the form of ammonium ions.
What role do decomposers play in the nitrogen cycle?
Detritus feeders or decomposers such as fungi and bacteria present in the soil convert the dead organic matter of plants or animals back into ammonia (NH3) or ammonium ions (NH4+).
What is the role of denitrifiers in the nitrogen cycle?
Denitrifiers such as Clostridium and Pseudomonas helps in the reduction ofnitrates (NO3) or nitrites (NO2), resulting in the escape of gaseous nitrogen which again returns to the cycle.
What is the role of lightening in the nitrogen cycle?
Lightning with thunderstorm serves as an important source of fixing nitrogen in the atmosphere apart from bacteria mediated nitrogen fixation. Here the energy of lightning breaks atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen oxides which can then be utilized by plants for assimilation.
Why is the nitrogen cycle important in nature?
- Allowing plants and animals to use nitrogen by converting atmospheric nitrogen to a more chemically available form such as ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3–), or organic nitrogen
- Enriching the soil through the formation of Nitrates and nitrites which are essential for the cultivation
- Helping in the synthesis of some biomolecules such as amino acids, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll, the building blocks of life
- Decomposing dead plant and animal matter by decomposers which cleans up the environment
How do humans impact the nitrogen cycle?
Human activities release excess nitrogen into the environment, eventually disturbing the balance of nitrogen in its different reservoirs in two possible ways:
- Burning of Fossil Fuels
- Use of Nitrogen-Containing Fertilizers
How does burning of fossil fuels affect the nitrogen cycle to cause climate change?
Burning fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gas releases excess nitrogen into the environment that accumulates over time. An increase in the concentration of nitrogen is found to affect the climate of the earth by gradually increasing its temperature, causing greenhouse effect and global warming.
How does the use of fertilizer affect the nitrogen cycle?
When artificial fertilizers containing nitrogen as one of the components are washed away from the agricultural fields, it contaminates the nearby water bodies and also the groundwater making it more difficult for the plants to absorb the nitrogen both for the terrestrial and aquatic plants. Since nitrogen fixation by plants is affected, it affects the nitrogen cycle.
Article was last reviewed on Tuesday, February 25, 2020




I liked this article .
Please, can you give me daily notifications
Thanks. Subscribe to our newsletter for getting update in your mail inbox.
its rilli an interesting source and user frienly with simple english
its really an interesting source and user friendly with simple English
Very simple explanation . Complete information on the topic presented
Thank you so much! Very helpful;)
thank you. very helpful
Very good explanation, keep it up