Radiant Flux
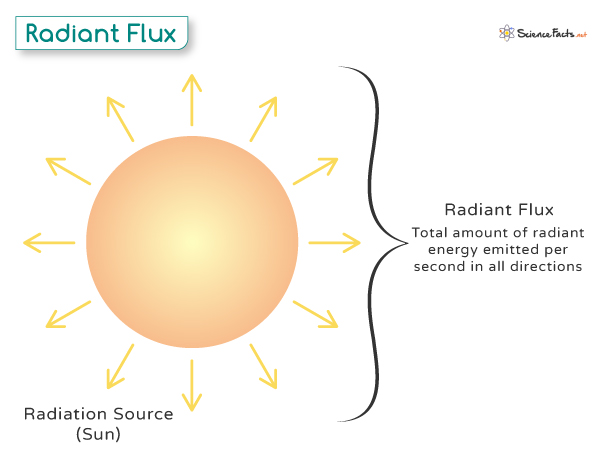
Radiant flux represents the total amount of radiation energy, including visible light, infrared, and ultraviolet, emitted, reflected, transmitted, or received by a surface or object per unit time. It measures the rate at which electromagnetic waves radiate or transfer energy, thereby calculating the power of light or electromagnetic radiation.
Imagine someone standing in the sunlight on a sunny day. The sunlight they feel on their skin is carrying energy. The amount of this energy hitting each square meter of their skin every second is the radiant flux.
Formula
The basic formula for radiant flux (Φ) is:
Where:
– S (λ) is the spectral power distribution, which tells us how much power is being carried by light at each wavelength (λ).
– λ1 and λ2 define the wavelength range of the radiation of interest. For example, to know the radiant flux of visible light, one must integrate over wavelengths from about 400 nm (blue) to 700 nm (red).
Units
The SI unit of radiant flux is Watt or W. One watt corresponds to one joule per second.
1 W = 1 J/s
It means that if a source emits or receives one joule of radiant energy every second, its radiant flux would be equivalent to one watt. The watt is often used to quantify the power output of devices such as light bulbs and lasers. When higher levels of radiant flux are involved, kilowatts (kW) or even megawatts (MW) may be used.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Wednesday, June 5, 2024