Radiant Intensity
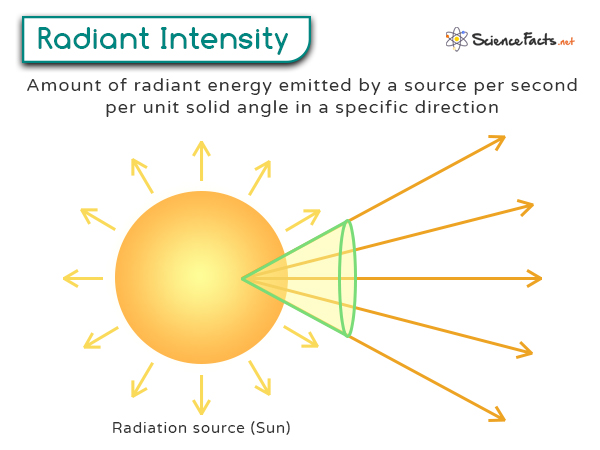
Radiant intensity is the radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted, or received per unit solid angle. It measures the power emitted by a radiation source in a given direction per unit solid angle.
For example, when you turn a flashlight on, it shines light in a particular direction. Radiant intensity tells us how much light power is being sent out in that direction. It is crucial to understand various aspects of light sources, such as flashlights, lasers, and LEDs.
Formula
The formula to calculate radiant intensity is:
I = P / Ω
Where:
– I is the radiant intensity in watts per steradian (W/sr)
– P is the total power emitted by the light source in watts (W)
– Ω denotes the solid angle in steradians (sr)
By understanding radiant intensity this way, it becomes easier to grasp how light sources are analyzed and compared based on how they emit light in specific directions
Units
The SI unit for radiant intensity is watts per steradian (W/sr). However, other common SI units used include milliwatts per steradian (mW/sr) and microwatts per steradian (μW/sr).
Applications
1. Lighting Design:
- To plan and implement lighting in buildings to achieve desired illumination effects and energy efficiency
- To design lighting setups to highlight performers and create specific visual effects on stage and theatre
2. Astronomy and Astrophysics:
- To measure the radiant intensity of celestial objects to determine their brightness and other properties
- To understand the emission characteristics of stars and planets by analyzing the radiant intensity of the light they emit
3. Medical Imaging:
- To produce clearer and more detailed images in imaging techniques such as X-rays and MRI
4. Weather and Climate:
- To study how sunlight interacts with the atmosphere to understand weather and climate and monitor changes in the environment.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Friday, June 7, 2024