Newton’s Third Law
What is Newton’s Third Law
Newton’s third law states that “If one object exerts a force on another object, then the other object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object”.
According to Newton’s third law, whenever two objects interact, they apply a force on each other. In other words, forces must always occur in pairs. These forces are known as action and reaction, and hence, another name for Newton’s third law is action-reaction law. Therefore, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Newton’s third law applies to bodies in rest or motion.
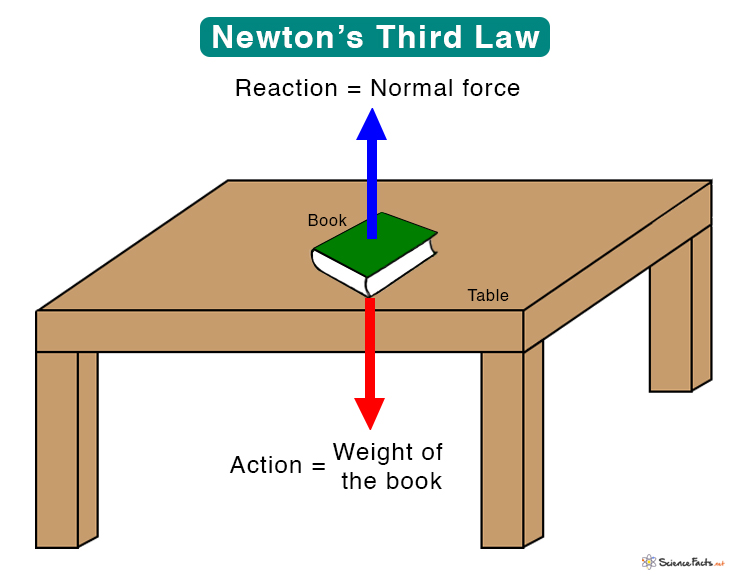
An example of Newton’s Third Law is a book lying on a table, as shown in the image below. The book applies a downward force on the table due to its weight (action). In response, the table exerts an equal and opposite upward force on the book (reaction). This upward force is called the normal force.
Newton’s Third Law Examples
1. Rocket Launch
A rocket’s thrust produces a large amount of force during launching. This force is responsible for lifting the rocket into space. Here, the thrust is the action, and the lift is the reaction. Both forces are equal and opposite.
2. Birds Flying
Birds can fly because of their wings. The wings push the air downwards. The air imparts an upward force on the wings allowing the birds to lift off the ground.
3. Car Moving
The wheels of a moving car push against the road with force. In turn, the road applies a forward friction force on the wheel that prevents the car from slipping. The two forces balance each other so that the car can ride smoothly without skidding. The wheel and axle is a simple device that obeys Newton’s third law.
4. Swimming
An example of Newton’s third law in sport is swimming. A swimmer pushes the water backward with his arms. The water reacts by applying a force in the forward direction enabling the swimmer to move ahead.
5. Earth and Moon
The Earth exerts a gravitational force on the Moon. The Moon exerts an equal and opposite force on Earth. The two forces are equal and opposite, thus enabling the Moon to revolve around the Earth’s orbit.
6. Two Magnets
When the like poles of two magnets are brought close to one another, they repel. The repulsive force exerted by the first magnet on the second is equal and opposite to the repulsive force exerted by the second magnet on the first.
7. Rowing a Boat
While rowing a boat, a person pushes the water backward with the oars. It is the action. The water applies an equal and opposite force on the boat that pushes the boat forward. It is the reaction.
Newton’s Third Law Equation
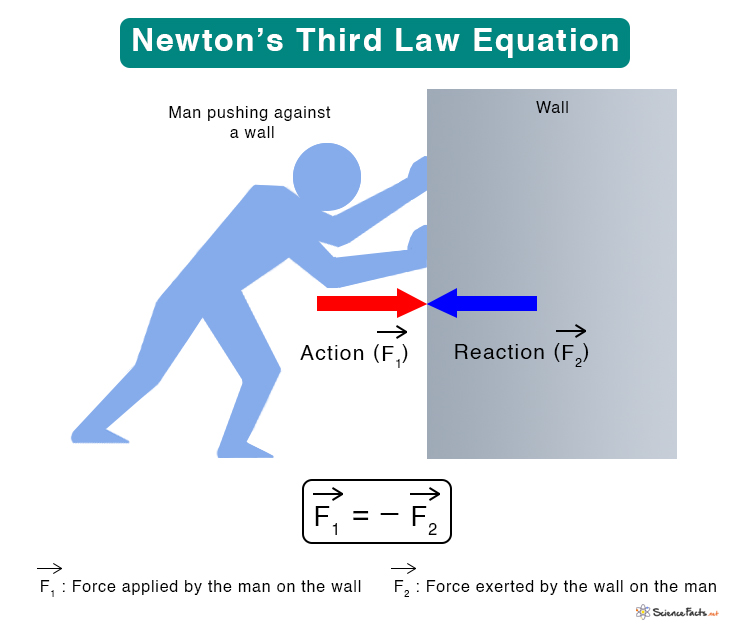
Suppose object A exerts force FAB on object B, and the latter exerts force FBA on the former. Then, Newton’s third law can be written as,
FAB = – FBA
In other words,
Action = – Reaction
The above diagram shows Newton’s third law equation by taking the example of a man pushing against the wall. In this case, the action is the person applying force F1 on the wall. The wall applies force F2 on the man, which is the reaction. According to the third law equation,
F1 = – F2
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Tuesday, December 10, 2024





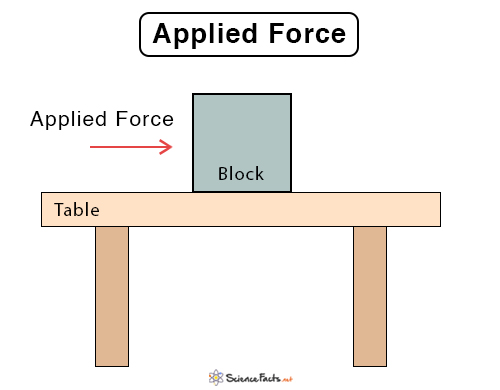
book on a table is NOT an example of N3L!!!!!! It is an example of balanced forces on a object.
The force pair for the book on the table is earth pulling the book down and the earth pulling the book up
Also the normal force of the book on the table is balanced my the normal force of the table on the book!
The book on table shows a pair of equal forces acting in opposite direction. The book exert force on the table, which is the action. The table responds by applying an equal and opposite force on the book, which is the reaction.
Earth pulls the book down, but Earth does not pull the book up. It it the normal force of support (table) that is the reaction to the Earth’s action force (gravity).
Newton’s third law states that “If one object exerts a force on another object, then the other object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object”.
However, in outer space there is not supposed to be any air molecules present. So the force coming from a spaceship is not exerting a force against any other object. So, it seems that Newton’s Third Law cannot apply to a spaceship using thrust in outer space. Any force coming from a spaceship simply would not propel that spaceship at all. Why does it seem like I am the only person that realizes this?
Lyudmil,
You are right. The earth does not exhibit a reaction to the book. It is a resistance to the force of the book being pulled toward earth.
Newton’s reaction is not a reaction at all but a resistance to force, also a reflection of a force. If no object or objects (like air molecules) are present to resist a force, then no action-reaction occurs.