Radiometry
Radiometry deals with the measurement and study of electromagnetic radiation, specifically focusing on the properties and behavior of light. It involves quantifying various radiometric quantities associated with the optical portion of electromagnetic radiation, which is further divided into ultraviolet, visible, and infrared.
Radiometry is important because it provides quantitative information about light and its interaction with matter. By accurately measuring these radiometric quantities, scientists can understand the physical characteristics and behaviors of light in different environments.
Radiometric Quantities
Radiometric quantities play a crucial role in accurately quantifying and analyzing various forms of radiant energy. The table below discusses these quantities.
| Radiometric Quantity | Definition | SI Unit (Symbol) |
|---|---|---|
| Radiant Energy | Total energy emitted by a source in the form of electromagnetic radiation | Joules or J |
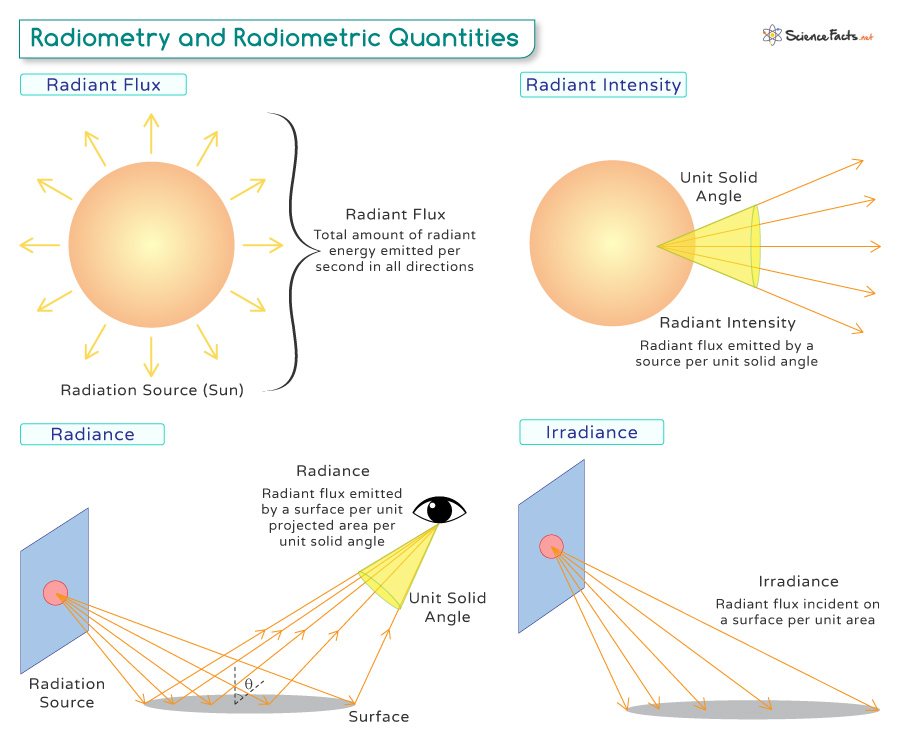
| Radiant Flux | Total amount of radiant energy emitted by a source per unit time | Watt (W) |
| Radiant Intensity | Amount of radiant flux emitted by a source per unit solid angle | Watt per steradian (W/sr) |
| Irradiance | Amount of radiant flux incident on a surface per unit area | Watts per square meter (W/m²) |
| Radiance | Radiant flux received by a surface per unit area per unit solid angle | Watts per square meter per steradian (W/(m²·sr)) |
| Radiant Exitance | Radiant flux emitted by a surface per unit area | Watts per square meter (W/m²) |
| Radiant Exposure | Radiant energy received by a surface per unit area | Watts per square meter (W/m²) |
| Spectral Flux | Radiant flux per unit wavelength | Watts per meter (W/m) |
| Spectral Intensity | Radiant intensity per unit wavelength | Watts per meter per steradian (W/m·sr) |
| Spectral Irradiance | Irradiance of a surface per unit wavelength | Watts per square meter per meter (W/m²·m), or W/(m²·nm) |
| Spectral Radiance | Radiance of a surface per unit wavelength | Watts per square meter per meter per steradian (W/m²·m·sr), or W/(m²·nm·sr) |
| Spectral Exitance | Radiant exitance per unit wavelength | Watts per square meter per meter (W/m²·m), or W/(m²·nm) |
| Spectral Exposure | Radiant exposure per unit wavelength | Joules per square meter per meter (J/m²·m), or J/(m²·nm) |
Applications
Radiometry is crucial in various fields, such as:
- Astronomy and Astrophysics: Radiometry helps physicists analyze starlight or other celestial emissions to determine their composition and physical properties.
- Meteorology: Weather forecasting or climate studies utilize radiometry to measure solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface or quantify atmospheric phenomena such as cloud cover.
- Photography and Cinematography: Proper exposure settings rely on accurately measuring the amount of light falling on a subject.
- Others: It is used across industries like agriculture to optimize crop growth using artificial lighting, aerospace for thermal analysis, telecommunications, and fiber optics, among many others.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Wednesday, June 5, 2024