Electrostatic Force
What is the Electrostatic Force?
The electrostatic force is the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged particles. It is also called Coulomb’s force or Coulomb’s interaction. For example, the force between the protons and electrons in an atom is electrostatic and is responsible for the atom’s stability. In chemistry, the electrostatic bonding force is important and binds an ionic molecule.
The laws of electrostatics were discovered by French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb in 1785 and are known as Coulomb’s law.
Laws Governing Electrostatic Force
Coulomb’s Law
The electrostatic force between two charged particles can be quantified by Coulomb’s law. It is usually applied to point charges and gives a relationship between the electrostatic force, the magnitude of the charges, and separation distance. According to this law, the force between the two particles is,
- Directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of the charges
- Inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two charges
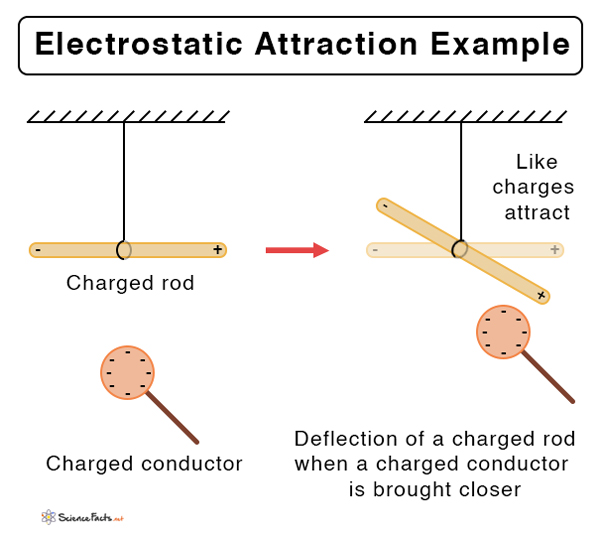
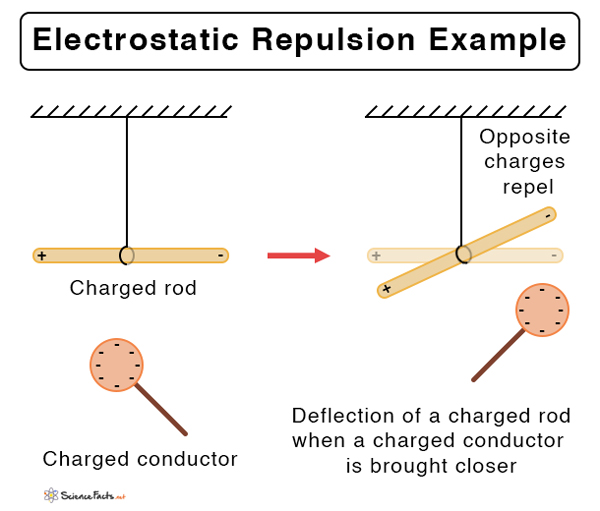
Suppose the two charged particles are brought close to one another. There will be an attraction if the charges are opposite, or if one is positive and the other negative. On the contrary, the charges will repel if both of them are positive or negative. In other words, like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
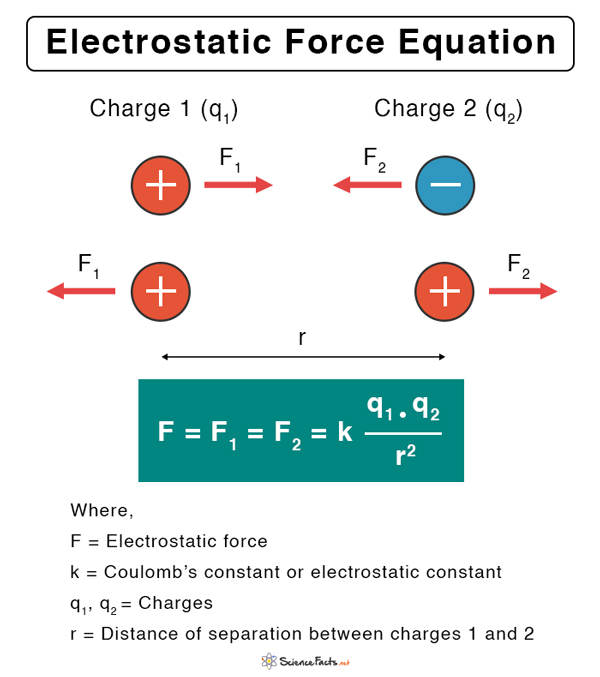
Electrostatic Force Equation
Let us assume that q1 and q2 are the amounts of charges on the two particles separated by a distance r. According to Coulomb’s law, the electrostatic force between the two charges is given by the following equation.
Electrostatic force unit: N (Newton).
Here, k is called Coulomb’s constant. Its value is 9 x 109 N.m2.C-2. Generally, q1 and q2 can be positive or negative. When two opposite point charges are placed close to each other, the force is attractive and hence, its sign is negative. The magnitude is merely the value of F without the sign. According to the above equation, F vanishes when r → ∞. Hence, at an infinitely large distance, the electrostatic force is zero. Technically, the range of F is infinite.
The work done W by the force F on a particle is the product of the force and the displacement d.
W= F x d
The work done in displacing the particle from one position to another is independent of the path taken. Hence, the electrostatic force is conservative.
Properties of Electrostatic Force
Here are some facts and characteristics of the electrostatic force.
- Like charges repel, and opposite charges attract
- Directly proportional to the product of two point-charges
- Inversely proportional to the distance of separation between the charges
- Acts along the line joining the two charges
Examples of Electrostatic Force in Daily Life
The electrostatic force is felt in everyday life situations. Here are a few examples, along with images.
- Rubbing of clouds generate charges. These charges will neutralize by passing through the atmosphere until they reach the neutral ground. We perceive this as lightning.
- After combing, if we bring the comb close to a piece of paper, there is a force of attraction between them.
- A silk shirt clings to the body because of charged particles on the shirt. The same applies to a woolen sweater when taking off.
- Getting out of a car on a warm, dry day and touching the door give us charges.
- Grains of sugar are attracted to the inside surface of a container due to electrostatic forces.
Applications of Electrostatic Force
Here are a few common applications of the electrostatic force.
- Photocopier
- Laser and ink-jet printers
- Van der Graaff generator
- Smoke precipitator and
- CCD camera
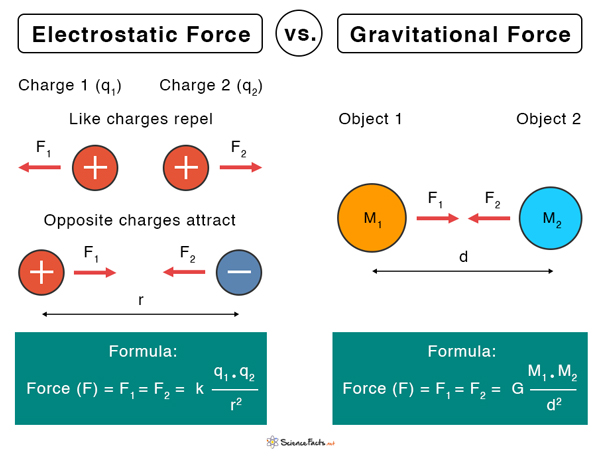
Difference between Electrostatic and Gravitational Forces
The electrostatic force and gravitational force are both fundamental forces of nature. There are a few similarities between the two as both follow the inverse-square law. However, there are also some critical differences.
Electrostatic Force vs. Gravitational Force | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties | Electrostatic Force | Gravitational Force |
| Due to | Electric charge | Mass |
| Strength | Strong | Weak |
| Dependency on medium | Depends upon the medium | Do not depend on the medium |
| Induction | Induction of charges is possible | There is no such concept as induction of masses |
| Nature | Attractive and repulsive | Attractive |
| Proportionality constant | k = 9 x 109 N.m2.C-2 | G = 6.67 X 10-11 N.m2.kg-2 |
| Magnitude | k q1 q2/d2 | G M1M2/R2 |
Electrostatic Force Problems and Solutions
Problem 1. What is the ratio of electrostatic force and gravitational force of two electrons?
Solution.
The ratio of electrostatic force to the gravitational force of two electrons is given by
FE/FG = ke2/Gme2
= 9 x 109 N.m2.C-2x (1.6 x 10-19)2 C2/6.67 x 10-11 N.m2.kg-2x (9.1 x 10-31)2 kg2
= 4 x 1042
Therefore, the relationship between the gravitational force and the electrostatic force is
FE = 4 x 1042 FG
Problem 2. If the electrostatic force between two charges is 124 N. What is the distance of separation between the charges, if the charges are 4 μC and 9 μC? Given k = 9 x 109 N m2.C-2.
Solution. We shall use the following equation.
F = k q1 q2/r2
Given, q1 = 4 x 10-6 C, q2 = 9 x 10-6 C, F = 124 N and k = 9 x 109 N m2.C-2. Putting these values,
124 N =9 x 109 N m2.C-2 x 9 x 10-6 C x 4 x 10-6 C / r2
Or, r2 = 9 x 109 N m2.C-2 x 9 x 10-6 C x 4 x 10-6 C / 124 N
= 0.00261 m2
Or, r = 0.05 m
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Friday, February 17, 2023







I have a problem with Formulas Of Electrostatics ????please can Somebody help me to Understand
May I know what problem you are facing?
I would like to know if we have a question that involves finding the coulombs force between charges and also the direction of force. so how do we find the direction (and i am in grade 10 so like we have to find without using any vector graph or else)
You can determine the direction of the electrostatic force using the rule that like charges repel and opposite charges attract. If both charges are positive or both are negative, they repel, meaning the force on each charge points away from the other. If one charge is positive and the other is negative, they attract, so the force on each charge points toward the other. The force always acts along the straight line connecting the two charges.