Types of Motion
What is Motion
A motion is defined by the change in an object’s position with time. Anything that moves is considered motion. Everything we see in front of us involves motion of some sort. A book falling off a table, the Moon revolving around the Earth, and a racing car on its track all describe motion. The physical quantities that define motion include distance, displacement, speed, and time.
What are the Types of Motion
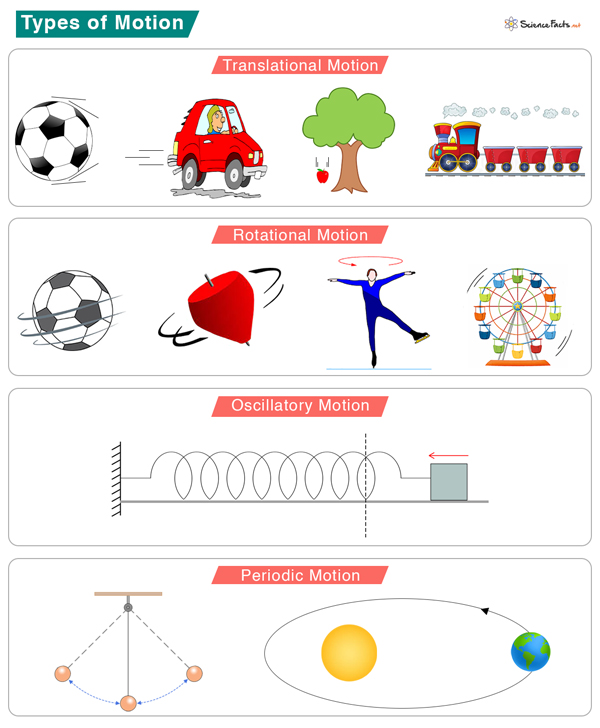
1. Translational Motion
In a translational motion, all points of a rigid body move in tandem. In other words, all points move with the same velocity. If the velocity changes or if the object accelerates, all points accelerate at the same time.
Translational motion can be rectilinear and curvilinear.
In a rectilinear motion, all points move in a straight line. For example, a train moving on its track or a bowling ball rolling down an alley.
In a curvilinear motion, all points move in a curved path. For example, a racing car near a turn or a merry-go-round.
2. Rotational Motion
In a rotational motion, all points of an object move in a circle. The rotation occurs about an axis; all points move with a common angular velocity. The axis remains fixed in space. For example, a spinning top or the Earth rotating about its axis.
3. Oscillatory Motion
In an oscillatory motion, the object moves back and forth about an equilibrium position. Such motion is possible only when a restoring force or torque acts on the object to bring it back to equilibrium. For example, water sprinklers or the vibrations of guitar strings.
4. Periodic Motion
In a periodic motion, the object’s motion is repeated over periodic time intervals. The time interval over which the motion recurs is called the time period. For example, a tuning fork or a simple pendulum.
Other types of motion include:
Uniform motion – When an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. For example, a car moves at a constant speed on the highway. The motion is termed uniform circular motion when the object moves in a circular path.
Non-uniform motion – When an object does not cover equal distances in equal time intervals. For example, a ball falls freely from the sky.
Projectile Motion – It describes the curved path of an object in free fall under the influence of gravity and initial velocity. For example, a ball can be thrown into the air at an angle of 45 degrees.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Friday, April 4, 2025